“My Pacakge” uses AdMob for showing ad in the application. The bad thing about AdMob library is it is not compatible with iOS 4 simulator (so many linking error occurs). I found the way to avoid these errors in the apple document. Switching code with pre-processor macros and exclude AdMob library from simulator build are the answer.
Compiling Source Code Conditionally for iOS Applications
There may be times when you need to run code on the simulator but not on a device, and the other way around. On those occasions, you can use the preprocessor macros TARGET_OS_IPHONE and TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR to conditionally compile code.
So I changed the code like below to remove AdMob lib dependency for the iPhone simulator build.
#if TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
UIView *ad;
#else
AdMobView *ad;
#endif
One more thing necessary for switching the code is library linking. Build setting needs conditional linking otherwise linking error occurs.
Opening Project info dialog then select Build tab. Find “Other Linker Flags” setting and select “Add Build Setting Condition” from Action menu (lower left corner menu).
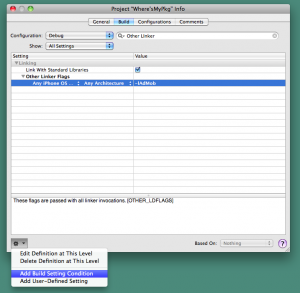
You can pick up conditions of sdk (device or simulator and its versions) and specify library or framework link settings (or other build settings).
Link:
Editing Conditional Build Settings (developer.apple.com)
Now you can automatically switch setting based on device or simulator.


